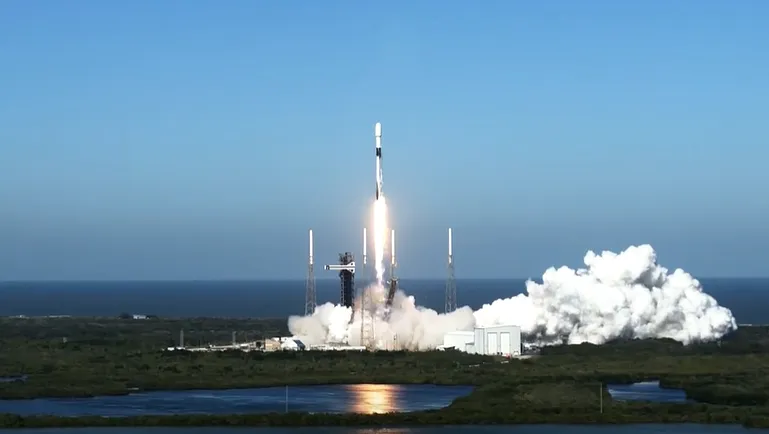
SpaceX, the renowned aerospace manufacturer and space transportation company, successfully launched an Indonesian communications satellite into orbit. This marks the 16th flight for SpaceX this year and the 300th successful Falcon 9 mission.
The satellite, which was launched from Cape Canaveral, is part of a broader effort to enhance Indonesia’s communication infrastructure. The mission was broadcasted live on Spaceflight Now, showcasing the Falcon 9 rocket’s powerful lift-off and the satellite’s journey into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
This successful launch is a testament to SpaceX’s continued growth and innovation in the field of space travel. The company, founded by Elon Musk, has been at the forefront of developing reusable rockets, which has significantly reduced the cost of space travel and made it more accessible to private companies and governments alike.
The Indonesian satellite launch also highlights SpaceX’s global impact, as the company continues to expand its reach and support various countries’ communication infrastructure. This particular mission was made possible by a Chinese rocket failure, which allowed SpaceX to step in and provide its services.
The Falcon 9 rocket, which has been used in over 100 missions, has become a symbol of SpaceX’s success. Its reusable design has made it possible for the company to offer cost-effective solutions for satellite launches, making it a popular choice for many companies and organizations.
The Indonesian satellite launch is just one of many successful missions for SpaceX this year. The company has continued to push the boundaries of space travel and has made significant strides in its mission to make space travel accessible to everyone.
In conclusion, SpaceX’s successful launch of the Indonesian communications satellite is a significant milestone for the company and the global space industry. As SpaceX continues to innovate and expand its reach, it is clear that the company will play a critical role in shaping the future of space travel and exploration.
A Brief History and Development of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 Rocket
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket, which has been used in over 100 missions, has become a symbol of SpaceX’s success and a critical component of the company’s growth. The Falcon 9 rocket was first introduced in 2010 and has since become one of the most reliable and cost-effective rockets in the industry.
The Falcon 9 rocket is a two-stage rocket, which means it has two main components: the first stage and the second stage. The first stage is designed to provide the initial thrust needed to lift the rocket off the ground, while the second stage continues the journey to orbit.
One of the key features of the Falcon 9 rocket is its reusable design. After the first stage separates from the second stage, it returns to Earth and lands vertically, allowing SpaceX to recover and reuse the rocket. This innovation has significantly reduced the cost of space travel and made it more accessible to private companies and governments alike.
The Falcon 9 rocket has undergone several upgrades and improvements since its introduction. In 2015, SpaceX introduced the Falcon 9 v1.1, which featured improved engines, a larger fuel tank, and a more powerful lift-off. In 2016, SpaceX introduced the Falcon 9 Full Thrust, which provided even more thrust and allowed for greater payload capacity.
In 2018, SpaceX introduced the Falcon 9 Block 5, which is the current version of the Falcon 9 rocket. The Block 5 features further improvements in engine performance, reusability, and payload capacity. The Block 5 is designed to be the final version of the Falcon 9 rocket, and SpaceX plans to use it for all future missions.
The Falcon 9 rocket has been instrumental in SpaceX’s success, enabling the company to offer cost-effective solutions for satellite launches and support various countries’ communication infrastructure. The rocket’s reusable design and continuous improvements have made it a popular choice for many companies and organizations, and it will continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of space travel and exploration.